Publications
Welcome to follow my work!
2024
-
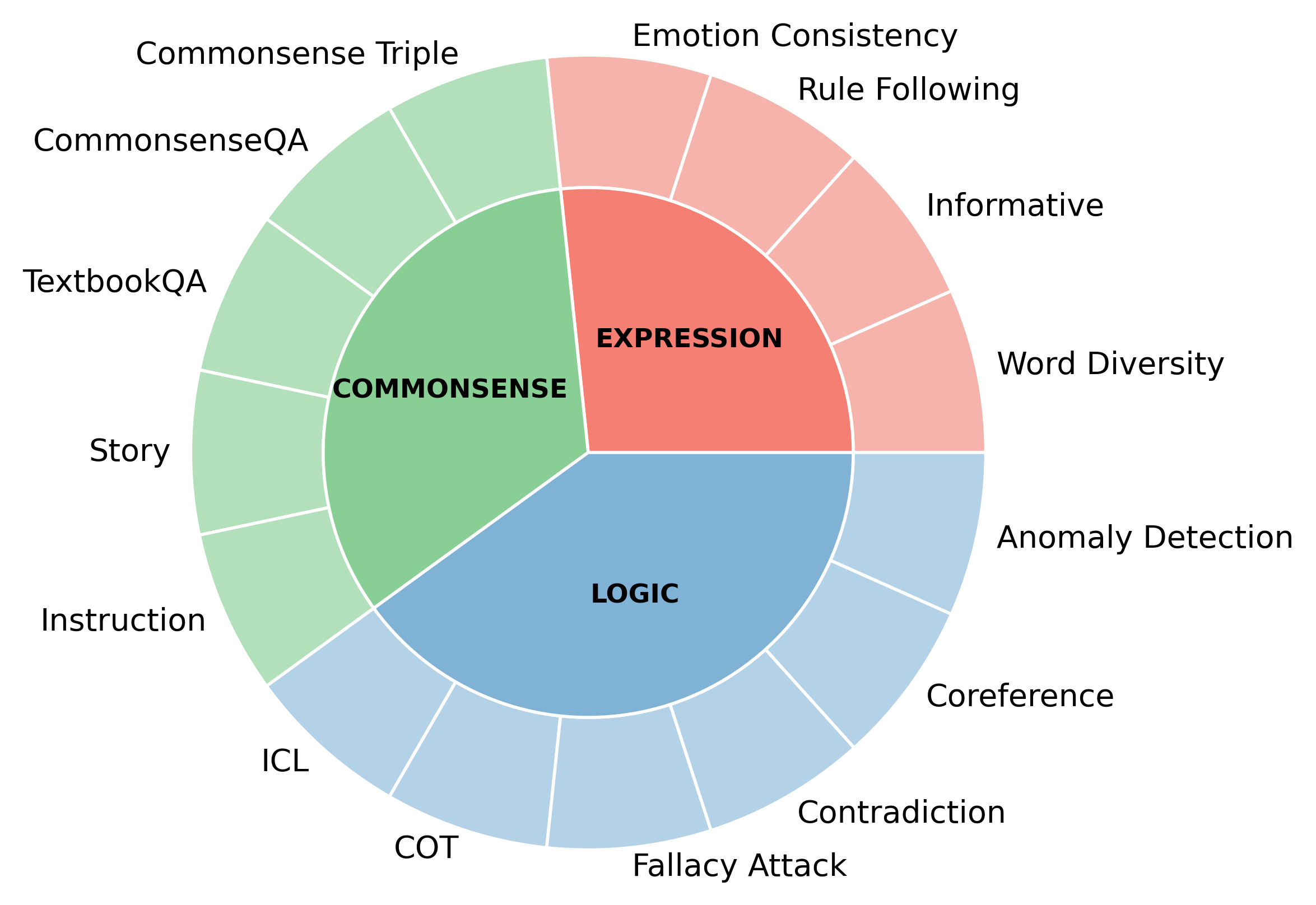 F-Eval: Asssessing Fundamental Abilities with Refined Evaluation MethodsYu Sun , Keyuchen Keyuchen , Shujie Wang , and 6 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) , Aug 2024
F-Eval: Asssessing Fundamental Abilities with Refined Evaluation MethodsYu Sun , Keyuchen Keyuchen , Shujie Wang , and 6 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) , Aug 2024Large language models (LLMs) garner significant attention for their unprecedented performance, leading to an increasing number of researches evaluating LLMs. However, these evaluation benchmarks are limited to assessing the instruction-following capabilities, overlooking the fundamental abilities that emerge during the pre-training stage. Previous subjective evaluation methods mainly reply on scoring by API models. However, in the absence of references, large models have shown limited ability to discern subtle differences. To bridge the gap, we propose F-Eval, a bilingual evaluation benchmark to evaluate the fundamental abilities, including expression, commonsense and logic. The tasks in F-Eval include multi-choice objective tasks, open-ended objective tasks, reference-based subjective tasks and reference-free subjective tasks. For reference-free subjective tasks, we devise new evaluation methods, serving as alternatives to scoring by API models. We conduct evaluations on 13 advanced LLMs. Results show that our evaluation methods show higher correlation coefficients and larger distinction than other evaluators. Additionally, we discuss the influence of different model sizes, dimensions, and normalization methods. We anticipate that F-Eval will facilitate the study of LLMs’ fundamental abilities.
@inproceedings{sun-etal-2024-f, title = {{F}-Eval: Asssessing Fundamental Abilities with Refined Evaluation Methods}, author = {Sun, Yu and Keyuchen, Keyuchen and Wang, Shujie and Li, Peiji and Guo, Qipeng and Yan, Hang and Qiu, Xipeng and Huang, Xuanjing and Lin, Dahua}, editor = {Ku, Lun-Wei and Martins, Andre and Srikumar, Vivek}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)}, month = aug, year = {2024}, address = {Bangkok, Thailand}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, pages = {9348--9369}, }
2023
-
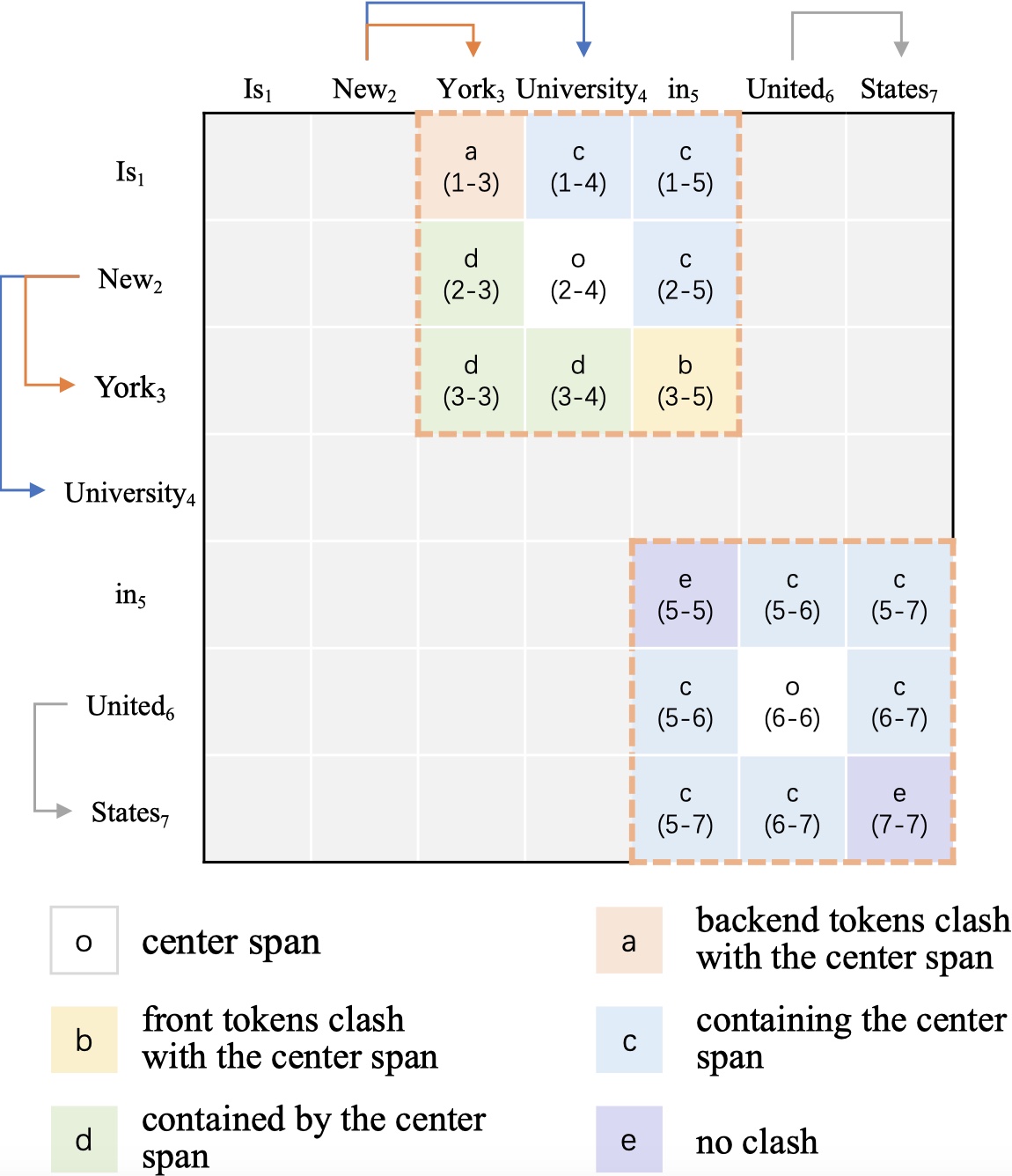 An Embarrassingly Easy but Strong Baseline for Nested Named Entity RecognitionHang Yan , Yu Sun , Xiaonan Li , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers) , Jul 2023
An Embarrassingly Easy but Strong Baseline for Nested Named Entity RecognitionHang Yan , Yu Sun , Xiaonan Li , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers) , Jul 2023Named entity recognition (NER) is the task to detect and classify entity spans in the text. When entity spans overlap between each other, the task is named as nested NER. Span-based methods have been widely used to tackle nested NER. Most of these methods get a score matrix, where each entry corresponds to a span. However, previous work ignores spatial relations in the score matrix. In this paper, we propose using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to model these spatial relations. Despite being simple, experiments in three commonly used nested NER datasets show that our model surpasses several recently proposed methods with the same pre-trained encoders. Further analysis shows that using CNN can help the model find more nested entities. Besides, we find that different papers use different sentence tokenizations for the three nested NER datasets, which will influence the comparison. Thus, we release a pre-processing script to facilitate future comparison.
@inproceedings{yan-etal-2023-embarrassingly, title = {An Embarrassingly Easy but Strong Baseline for Nested Named Entity Recognition}, author = {Yan, Hang and Sun, Yu and Li, Xiaonan and Qiu, Xipeng}, editor = {Rogers, Anna and Boyd-Graber, Jordan and Okazaki, Naoaki}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers)}, month = jul, year = {2023}, address = {Toronto, Canada}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, doi = {10.18653/v1/2023.acl-short.123}, pages = {1442--1452}, } -
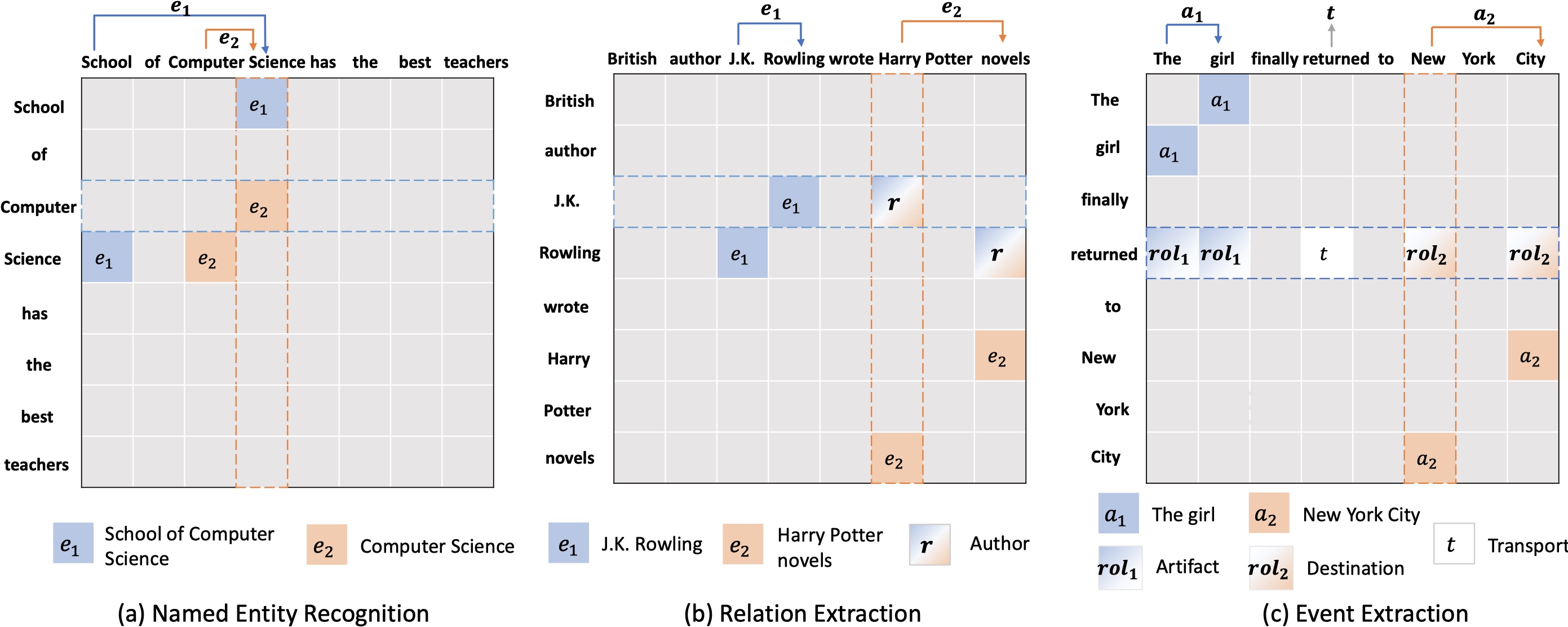 UTC-IE: A Unified Token-pair Classification Architecture for Information ExtractionHang Yan , Yu Sun , Xiaonan Li , and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) , Jul 2023
UTC-IE: A Unified Token-pair Classification Architecture for Information ExtractionHang Yan , Yu Sun , Xiaonan Li , and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) , Jul 2023Information Extraction (IE) spans several tasks with different output structures, such as named entity recognition, relation extraction and event extraction. Previously, those tasks were solved with different models because of diverse task output structures. Through re-examining IE tasks, we find that all of them can be interpreted as extracting spans and span relations. They can further be decomposed into token-pair classification tasks by using the start and end token of a span to pinpoint the span, and using the start-to-start and end-to-end token pairs of two spans to determine the relation. Based on the reformulation, we propose a Unified Token-pair Classification architecture for Information Extraction (UTC-IE), where we introduce Plusformer on top of the token-pair feature matrix. Specifically, it models axis-aware interaction with plus-shaped self-attention and local interaction with Convolutional Neural Network over token pairs. Experiments show that our approach outperforms task-specific and unified models on all tasks in 10 datasets, and achieves better or comparable results on 2 joint IE datasets. Moreover, UTC-IE speeds up over state-of-the-art models on IE tasks significantly in most datasets, which verifies the effectiveness of our architecture.
@inproceedings{yan-etal-2023-utc, title = {{UTC}-{IE}: A Unified Token-pair Classification Architecture for Information Extraction}, author = {Yan, Hang and Sun, Yu and Li, Xiaonan and Zhou, Yunhua and Huang, Xuanjing and Qiu, Xipeng}, editor = {Rogers, Anna and Boyd-Graber, Jordan and Okazaki, Naoaki}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)}, month = jul, year = {2023}, address = {Toronto, Canada}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, doi = {10.18653/v1/2023.acl-long.226}, pages = {4096--4122}, } -
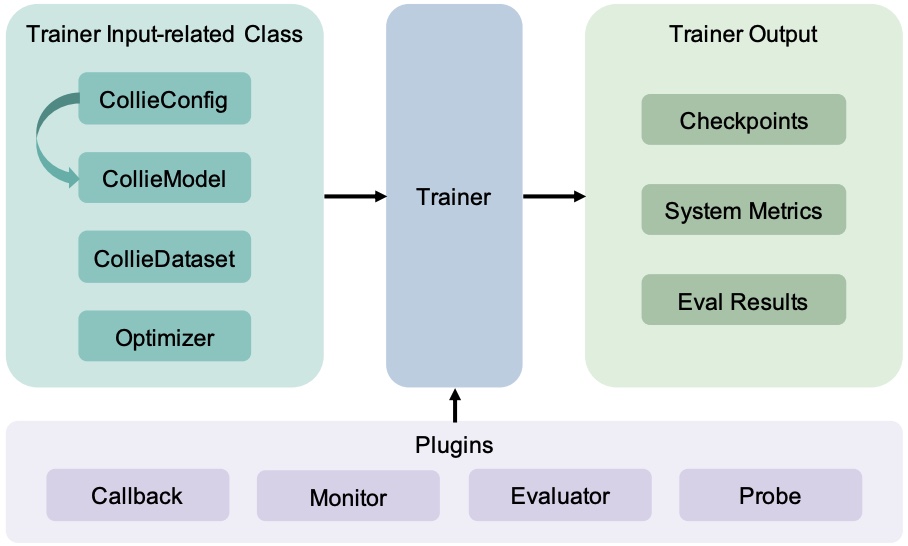 CoLLiE: Collaborative Training of Large Language Models in an Efficient WayKai Lv , Shuo Zhang , Tianle Gu , and 11 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations , Dec 2023
CoLLiE: Collaborative Training of Large Language Models in an Efficient WayKai Lv , Shuo Zhang , Tianle Gu , and 11 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations , Dec 2023Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly pivotal in a wide range of natural language processing tasks. Access to pre-trained models, courtesy of the open-source community, has made it possible to adapt these models to specific applications for enhanced performance. However, the substantial resources required for training these models necessitate efficient solutions. This paper introduces CoLLiE, an efficient library that facilitates collaborative training of large language models using 3D parallelism, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, and optimizers such as Lion, Adan, Sophia, and LOMO. With its modular design and comprehensive functionality, CoLLiE offers a balanced blend of efficiency, ease of use, and customization. CoLLiE has proven superior training efficiency in comparison with prevalent solutions in pre-training and fine-tuning scenarios. Furthermore, we provide an empirical evaluation of the correlation between model size and GPU memory consumption under different optimization methods, as well as an analysis of the throughput. Lastly, we carry out a comprehensive comparison of various optimizers and PEFT methods within the instruction-tuning context. CoLLiE is available at https://github.com/OpenLMLab/collie.
@inproceedings{lv-etal-2023-collie, title = {{C}o{LL}i{E}: Collaborative Training of Large Language Models in an Efficient Way}, author = {Lv, Kai and Zhang, Shuo and Gu, Tianle and Xing, Shuhao and Hong, Jiawei and Chen, Keyu and Liu, Xiaoran and Yang, Yuqing and Guo, Honglin and Liu, Tengxiao and Sun, Yu and Guo, Qipeng and Yan, Hang and Qiu, Xipeng}, editor = {Feng, Yansong and Lefever, Els}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations}, month = dec, year = {2023}, address = {Singapore}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, doi = {10.18653/v1/2023.emnlp-demo.48}, pages = {527--542}, }
2022
-
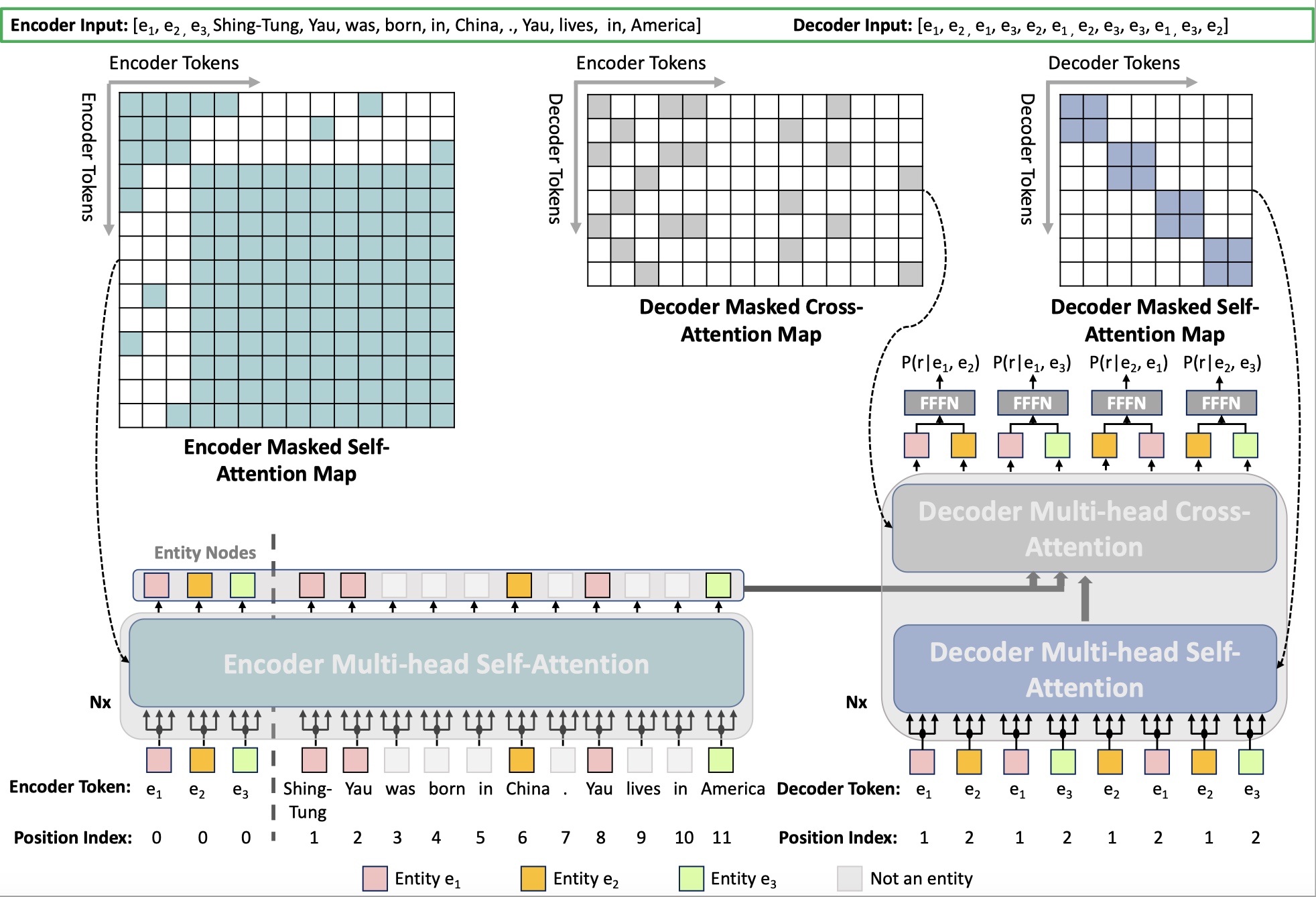 BART-Reader: Predicting Relations Between Entities via Reading Their Document-Level Context InformationHang Yan , Yu Sun , Junqi Dai , and 4 more authorsIn Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing , Dec 2022
BART-Reader: Predicting Relations Between Entities via Reading Their Document-Level Context InformationHang Yan , Yu Sun , Junqi Dai , and 4 more authorsIn Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing , Dec 2022Document-level relation extraction (Doc-RE) aims to classify relations between entities spread over multiple sentences. When one entity is paired with separate entities, the importance of its mentions varies, which means the entity representation should be different. However, most of the previous RE models failed to make the relation classification entity-pair aware effectively. To that end, we propose a novel adaptation to simultaneously utilize the encoder and decoder of the sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) pre-trained model BART in a non-generative manner to tackle the Doc-RE task. The encoder encodes the document to get the entity-aware contextualized mention representation. The decoder uses a non-causal self-attention mechanism and masked cross-attention to model the interactions between the entity pair under consideration explicitly. By doing so, we can fully take advantage of the pre-trained model in the encoder and decoder sides. And experiments in three Doc-RE datasets show that our model can not only take more advantage of BART, but surpass various BERT and RoBERTa based models.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-031-17120-8_13, author = {Yan, Hang and Sun, Yu and Dai, Junqi and Hu, Xiangkun and Guo, Qipeng and Qiu, Xipeng and Huang, Xuanjing}, editor = {Lu, Wei and Huang, Shujian and Hong, Yu and Zhou, Xiabing}, title = {BART-Reader: Predicting Relations Between Entities via Reading Their Document-Level Context Information}, booktitle = {Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing}, year = {2022}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {159--171}, isbn = {978-3-031-17120-8}, } -
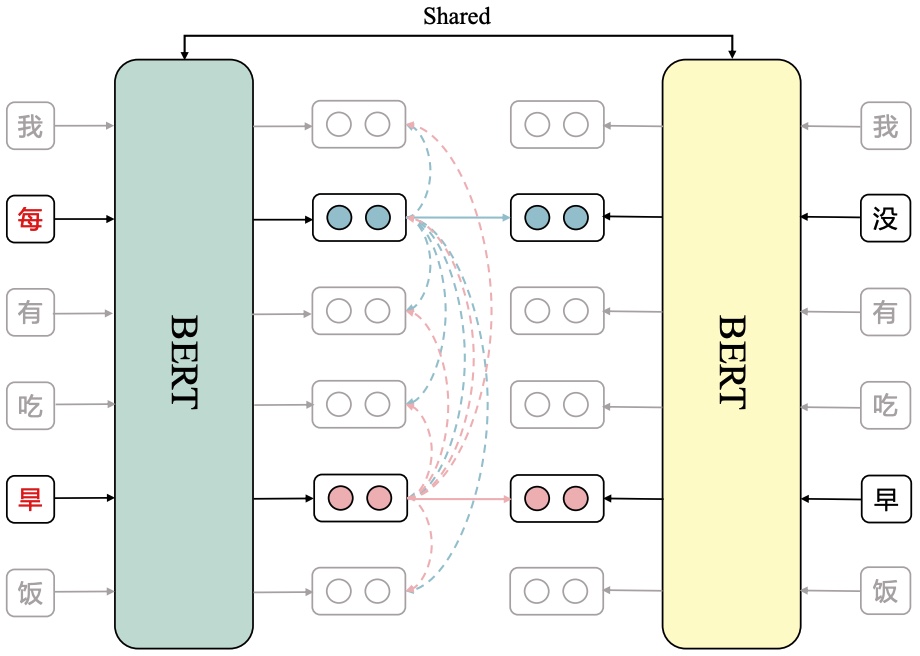 SDCL: Self-Distillation Contrastive Learning for Chinese Spell CheckingXiaotian Zhang , Hang Yan , Yu Sun , and 1 more authorDec 2022
SDCL: Self-Distillation Contrastive Learning for Chinese Spell CheckingXiaotian Zhang , Hang Yan , Yu Sun , and 1 more authorDec 2022@misc{zhang2022sdcl, title = {SDCL: Self-Distillation Contrastive Learning for Chinese Spell Checking}, author = {Zhang, Xiaotian and Yan, Hang and Sun, Yu and Qiu, Xipeng}, year = {2022}, eprint = {2210.17168}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.CL}, }